Introduction:-
The gas turbine is the engine at the heart of the power plant that produces electric current.A gas turbine is a combustion engine that can convert
natural gas or other liquid fuels to mechanical energy. This energy then drives a generator that produces electrical energy. It is electrical energy that moves along power lines to homes and businesses.
natural gas or other liquid fuels to mechanical energy. This energy then drives a generator that produces electrical energy. It is electrical energy that moves along power lines to homes and businesses.
HOW GAS TURBINE POWER PLANTS WORK:-
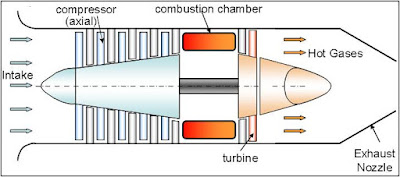
The combustion (gas) turbines being installed in many of today's natural-gas-fueled power plants are complex machines, but they basically involve three main sections:
- The compressor, which draws air into the engine, pressurizes it, and feeds it to the combustion chamber at speeds of hundreds of miles per hour.
- The combustion system, typically made up of a ring of fuel injectors that inject a steady stream of fuel into combustion chambers where it mixes with the air. The mixture is burned at temperatures of more than 2000 degrees F. The combustion produces a high temperature, high pressure gas stream that enters and expands through the turbine section.
- The turbine is an intricate array of alternate stationary and rotating aerofoil-section blades. As hot combustion gas expands through the turbine, it spins the rotating blades. The rotating blades perform a dual function: they drive the compressor to draw more pressurized air into the combustion section, and they spin a generator to produce electricity.
To generate electricity, the gas turbine heats a mixture of air and fuel at very high temperatures, causing the turbine blades to spin. The spinning turbine drives a generator that converts the energy into electricity.
The gas turbine can be used in combination with a steam turbine—in a combined-cycle power plant—to create power extremely efficiently.
- Air-fuel mixture ignites.
- The gas turbine compresses air and mixes it with fuel that is then burned at extremely high temperatures, creating a hot gas.
- Hot gas spins turbine blades.
- The hot air-and-fuel mixture moves through blades in the turbine, causing them to spin quickly.
- Spinning blades turn the drive shaft.
- The fast-spinning turbine blades rotate the turbine drive shaft.
- Turbine rotation powers the generator.
- The spinning turbine is connected to the rod in a generator that turns a large magnet surrounded by coils of copper wire.
- Generator magnet causes electrons to move and creates electricity.
- The fast-revolving generator magnet creates a powerful magnetic field that lines up the electrons around the copper coils and causes them to move.
- The movement of these electrons through a wire is electricity.


No comments:
Post a Comment