Adaptive Headlight System :-
Suppose you are driving home from a weekend vacation. It's late at night, and the winding two-lane road has no streetlights. You approach a curve at 40 mph -- slow enough to make the turn, but too fast to stop suddenly if you need to.
In this case what would you do ?

One option is to slow down your vehicle and look what is in front as headlights are focusing in straight line.
Second option is to go with adaptive headlight system.
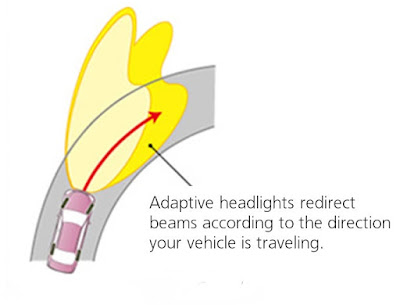
Standard headlights shine straight ahead, no matter what direction the car is moving. When going around curves, they illuminate the side of the road more than the road itself. Similarly, when a vehicle with standard headlights crests a hill, the headlight beams temporarily point upwards towards the sky. This makes it difficult for drivers to see the road ahead and for oncoming motorists to see the driver approaching.Adaptive headlights react to the steering, speed and elevation of the car and automatically adjust to illuminate the road ahead. When the car turns right, the headlights angle to the right. Turn the car left, the headlights angle to the left. This is important not only for the driver of the car with adaptive headlights, but for other drivers on the road as well. The glare of oncoming headlights can cause serious visibility problems. Since adaptive headlights are directed at the road, the incidence of glare is reduced.
A car with adaptive headlights uses electronic sensors to detect the speed of the car, how far the driver has turned the steering wheel, and the yaw of the car. Yaw is the rotation of the car around the vertical axis -- when a car is spinning, for example, its yaw is changing. The sensors direct small electric motors built into the headlight casing to turn the headlights. A typical adaptive headlight can turn the lights up to 15 degrees from center, giving them a 30-degree range of movement.
Suppose you are driving home from a weekend vacation. It's late at night, and the winding two-lane road has no streetlights. You approach a curve at 40 mph -- slow enough to make the turn, but too fast to stop suddenly if you need to.
In this case what would you do ?

One option is to slow down your vehicle and look what is in front as headlights are focusing in straight line.
Second option is to go with adaptive headlight system.
Standard headlights shine straight ahead, no matter what direction the car is moving. When going around curves, they illuminate the side of the road more than the road itself. Similarly, when a vehicle with standard headlights crests a hill, the headlight beams temporarily point upwards towards the sky. This makes it difficult for drivers to see the road ahead and for oncoming motorists to see the driver approaching.Adaptive headlights react to the steering, speed and elevation of the car and automatically adjust to illuminate the road ahead. When the car turns right, the headlights angle to the right. Turn the car left, the headlights angle to the left. This is important not only for the driver of the car with adaptive headlights, but for other drivers on the road as well. The glare of oncoming headlights can cause serious visibility problems. Since adaptive headlights are directed at the road, the incidence of glare is reduced.
A car with adaptive headlights uses electronic sensors to detect the speed of the car, how far the driver has turned the steering wheel, and the yaw of the car. Yaw is the rotation of the car around the vertical axis -- when a car is spinning, for example, its yaw is changing. The sensors direct small electric motors built into the headlight casing to turn the headlights. A typical adaptive headlight can turn the lights up to 15 degrees from center, giving them a 30-degree range of movement.
Adaptive headlights also benefit other motorists on the road. For example, when a vehicle turns around a bend in low-light conditions, standard headlights will temporarily point directly at oncoming traffic. This can lead to discomfort and temporary blindness for oncoming motorists. This problem is avoided with adaptive headlights, since their beams stay on the road and do not point at oncoming traffic. In addition, since headlight beams to not point at other motorists, it is safe for drivers who own a vehicle with adaptive headlights to use bi-xenon lights. Emitting a slightly blue-ish tint, these lights are brighter than standard lights and offer a clearer, more distinct view of the road ahead.